Page 132 - RoboCilindri, RCP2-RCP3, robocilindri, sinta,
P. 132
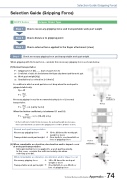
Selection Guide (Gripping Force)Selection Guide (Gripping Force)RCP2 SeriesGripper Slider TypeStep 1Step 2Step 3Step 1Check necessary gripping force and transportable work part weightCheck distance to gripping pointCheck external force applied to the finger attachment (claw)Check necessary gripping force and transportable work part weightWhen gripping with frictional force, calculate the necessary gripping force as shown below.(1) Normal transportationF : Gripping force [N] ...... Sum of push forcesCoefficient of static friction between the finger attachment and the work partm : Work part weight [Kg]g : Gravitational acceleration [= 9.8m/s2]A condition in which a work part does not drop when the work part is gripped statistically:F > mgNecessary gripping force as the recommended safety factor of 2 in normal transportation:F > mg x 2 (safety factor)F/2F/2FrictionW (mg)F >mg 0.1~0.2x 2 = (10~20) x mg* As the Coefficient of static friction increases, the work part weight also increases. Select a model which can achieve the gripping force of 10 to 20 times or more.(2) When remarkable acceleration, deceleration and/or impact occur at work part transportationStronger inertial force is applied to a work part by gravity. In this case, consider the sufficient safety rate when selecting a model.FrictionNormal work part transportationNecessary gripping force 10 to 20 times the work part weight or moreTransportable work part weight One-tenth to one-twentieth or less of gripping forceF/3W (mg)F/3F/3When remarkable acceleration, deceleration and/or impact occurNecessary gripping force 30 to 50 times the work part weight or moreTransportable work part weight One-thirtieth to one-fiftieth or less of gripping forceTechnical Reference/Information Appendix: - 74